Growth and Development Assessment Notes
Birth Weight
- Always plot on Growth Chart
- Infants double weight by 6 months
- Infants triple weight by 12 months
- Remember pediatric obesity has increased to 20-25% which is causing an increased risk for diabetes and hypertension
- 0 to 6 months: 6-8 oz per week and 1in per month
- 6 to 12 months: 3-4 oz per week and ½ inch per month
- Neonates lose up to 7% of body weight but should regain it by the 2 weeks of age.
Head Circumference
- HC is always measured and plotted from birth until 3 years of age using a paper tape also known as occipitofrontal circumference/
- Use paper tape ( Cloth tapes) always place above the ears
- HC is always measures at the largest circumference, above the ear
- HC in newborn is 1-2 cm larger than chest circumference
- HC will > by 12 cm during the first 12 months
- Fastest rate of head growth is during the first 3 months of life 2 cm per month.
Feeding Schedule
- Breastfeeding preferred over formula. If formula is choses start with one fortified with iron
- Give Vitamin D drops (minimum of 200IU) within the first few days of life if breastfeeding because breast milk alone does not provide adequate levels of vitamins. Infant formula is supplemented with Vitamin D.
- Breast milk or formula contains 20cal per oz it also decrease the risk of infections during the first few weeks of life
- Avoid Cow’s milk the first year of life cause it causes GI bleeding it also causes iron deficiency in babies younger than 12 months
- Start solid foods @ 4-6 months. Start with rice cereal before other types of cereals or good groups. Introduce one food at a time for 4-5 days ( if allergic easier to identify offending food
Primary Dentition Occur/ Dental Health
- Fist dentition (first tooth) about 6 months
- Both left and right teeth erupt bilaterally at the same time. S/s consist of drooling, chewing on objects, irritability, crying and fever
- 6 – 10 months of age lower central incisors ( lower front teeth)
- Final primary teeth happens around 20 teeth. They have a complete set of primary teeth ( 20 teeth)
- First permanent teeth which consist of central incisors and first molars happen around 6 years of age
- Fluoride supplementation starts at 6 months
Head to Toe Examination
- Always look for a funny looking baby
- Assess reflex in newborn such as (Moro, Stepping, Palmar/ Planter Grasps) you are assessing neurologic development * muscle tone and symmetry, ROM
- Cardiac Murmurs * remember murmurs are common 10% significant due to growing and stretching of vessels, valves and chambers ( refer murmur > grade II)
- Testes should descend by 1 year of age
- Hearing and Visual Tracking mist speech and language develop by age 3. Pediatric hearing loss is associated with speech delay
Vision Evaluation
- 1 month infants can brief fixate eyes on mother face
- 3 months infant will hold its hand close to face to observe. Try holding a bright object or a toy in front of infant. Avoid using toys that makes noise or objects
- 6 month make good eye contact. Scan surrounding up to 180 degree visual field
- 12 months make prolonged eye contact when spoken to. Will actually turn head around 180 degrees to observe people and surrounding for long periods. Recognize parents and favorite people from a long distance
- Strabismus is an ocular misalignment, meaning that one eye turns inward or outward. This prevents the eyes from focusing together on an image and can cause double vision (Diplopia). If left uncorrected can result in permeant visual loss and abnormal vison.
- To assess for this use Cover/ Uncover test (6 Months to 3 years of age) * Remember can’t assess before then because the ocular muscle is not mature yet.
- Newborn Vision are nearsighted (myopia) and have a vision of 30/400. During the 1st two months the infants eyes may cross at times are normal findings. If one eye consistently turned inwards or outward REFER
- Newborns do not shed tears because the lacrimal ducts are not fully mature yet
- Vison Screen starts at age 3-4 years of age
- Vision @ 3 years 20/50, Vison @ 4 years 20/40, @ 5 years 20/30 ,@ 6 years 20/20 normal vison
Routine Screening
- Height, Weight HC and BMI @ every visit
- HCT screening starts @ 9 months because a healthy newborn has iron store that last up to 6 months. Check ranges according to the age of child. No screening @ birth because of elevation from maternal RBC mixed in fetal RBC
- High risk children should be screen at age 1 to 2 years of age (lead levels > 10)
- Cholesterol screening is recommended for children ONLY with a family with hx of premature CV disease
- Routine BP should start @ age 3 years of age. Systolic BP= 2 X(YEARS) +80 Diastolic BP = 2/3 systolic
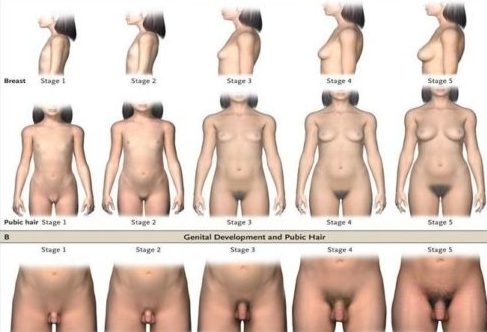
Tanner Staging
Girls Breast:
Stage 1: Prepuberty
Stage 2: Breast bud (onset of breast development)
Stage 3: Breast and Areola are in one mound
Stage 4: Breast and Areola are form a second mound
Stage 5: Adult Pattern
Boy’s external genital:
Stage 1: Prepuberty
Stage 2: Testes begin to enlarge scrotum skin redden and change in texture
Stage 3: Penis lengths
Stage 4: Penis widens and scrotum skin gets darker
Stage 5: Adult Pattern
Girls/Boys Pubic Hair:
Stage 1: Prepuberty
Stage 2: Sparse Growth of straight hair that is easily counted
Stage 3: Hair darker and starts to curl dark course
Stage 4: Thicker curly hair but not on my medial thigh. Hair is course
Stage 5: Adult pattern Inner Thigh
Immunization Schedule
- Live Attenuated Vaccines are MMR, Varicella. Do not give immunocomprised individual
- DTaP ( Diptheria, Tetanus, Pertussis)
- Hib ( H Influenza- type B) prevent meningitis
- Hep B ( Prevent Hepatitis B)
- Prevnar ( Pneumoccal ) Prevent Bacterial Meningitis
- Influenza ( Prevent Flu)
- Comvax is a combination of Haemophilus B and Hep B the advantage of it reduces the number of injections the child gets at one time
Rules of Childhood Immunization:
- Minimum of 4-6 weeks between Vaccines
- No MMR before 12 months of age
- No MMR in pregnancy
- NO MMR or Influenza if egg allergy
- HIB is not given past 5 years of age
- Dtap repeated every 10 years because of recent outbreak of Pertussis
HPV Vaccine
- Recommended for 11-12 year girls but can be given as young as 9. Also recommend for age 13-26 if they have not received the vaccine at all or have not complete the vaccine
- Why recommended for young girls: they should get it before becoming sexually active. The vaccine is most effective in girl/women who have not yet acquired any of the four HPV types covered by the vaccine. Girls/women who have not been infected with any of those four HPV types will get the full benefits of the vaccine
- Sexually active females benefit from the vaccine: yes they may benefit from it but they will get less benefit from the vaccine since they have already acquired one or more of the HPV types covered by the vaccine. Few women are infected with all four types. So they will still get some type of protection.
- HPV vaccine only recommended for girls/women ages 9 to 26: Research showed the vaccine safety and efficacy has only recently begin with women older than 26 years of age
- HPV has been approved for boys in 2009
- Pregnancy women get the vaccine? : Not recommended the woman should complete their pregnancy first before getting vaccine. If the women finds out she is pregnant
After she has started the vaccine series she should complete her pregnancy before finishing the three dose series
- Research studies shown the vaccine have been 100% effective in preventing the dx cause by four HPV types including the precancers for the cervix, vulva, and vagina and genital warts. The study has been mainly studied in women who has not been exposed
- Vaccine was less effective in young women who have been already been exposed to one of the HPV types covered by the vaccine
- The vaccine does not treat existing HPV infections, genital warts, precancers or cancers
- How long does the vaccine protection last? Will booster be needed: its unknown. So far studies have shown for at least 5 years women were found to be still protected. More research is being done to find out how long protection will last and if even booster vaccine is needed.
- What does the vaccine not protect against: About 30% of cervical cancer or genital warts. It important for women to continue to get screened for cervical cancer regular Pap smear Test. It will not prevent about 10% genital wats nor other STD. So it will still be important for sexually active adults to reduce exposure to HPV and other STD
- IF a girl/women does not get all 3 doses how much protection again HPV will they get?; its not yet known. Very Important to get all 3 doses
HPV is given through a series of 3 shots over 6 month period. The second and third doses should be gi