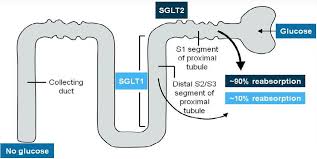
SGLT2 inhibitors are a newer drug class with a less certain long-term safety profile. SGLT2 is a low-affinity, high capacity glucose transporter located in the proximal tubule in the kidneys. It is responsible for 90% of glucose reabsorption. Inhibition of SGLT2 leads to the decrease in blood glucose due to the increase in renal glucose excretion. The mechanism of action of these drugs gives further glucose control by allowing increased insulin sensitivity and uptake of glucose in the muscle cells, decreased gluconeogenesis and improved first phase insulin release from the beta cells.
empagliflozin was shown in one trial to reduce cardiovascular risk in people with CVD and type 2 diabetes. Adverse effects for SGLT2 inhibitors included a higher rate of genital infections, DKA, acute kidney injury, fracture, and/or amputation. inhibits sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2), reducing glucose reabsorption and increasing urinary glucose excretion. SGLT2 inhibitors control blood sugar levels by excreating of glucose by the kidneys. SGLT2 inhibitors are not used in the treatment of Type 1 DM.
Contradictions
- Hypersensitivity to drug
- pregnancy 2nd or 3rd trimester
- diabetes mellitus, type 1
- diabetic ketoacidosis
- active bladder CA
- volume depletion
- GFR <60
Serious Reactions
hypersensitivity reaction
anaphylaxis
acute renal failure
renal impairment
ketoacidosis
complicated UTI’s
hypotension, orthostatic
bladder CA risk
Common Reactions
genital mycotic infection
nasopharyngitis
UTI
back pain
increase urination
nausea
influenza
increase in cholesterol
constipation
urinary discomfort
extremity pain
Increase Cre
hypotension, orthostatic
Monitoring
GFR at baseline, then periodically
BP
lipid panel
SGLT2 inhibitor drugs class include
Empagliflozin (Jardiance)
Dapagliflozin (Farxiga)
Ipragliflozin (which has not yet been approved for use in the U.S.)
Canagliflozin (Invokana)
Combination Drugs
Invokamet = canagliflozin and metformin
Xigduo XR = dapagliflozin and metformin extended-release
Glyxambi = empagliflozin and linagliptin
References
“Canagliflozin Provided Substantial and Sustained Glycemic Improvements as Monotherapy and in Add-On Combinations in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes in Five Phase 3 Studies.” Johnson & Johnson. Jansen Research & Development, 09 June 2012. Web. 02 Apr. 2013.
Clarke, Toni. “FDA Approves Johnson & Johnson Diabetes Drug, Canagliflozin.” Reuters. Thomson Reuters, 29 Mar. 2013. Web. 01 Apr. 2013.
“Diabetes Treatment, Part 2: Oral Agents for Glycemic Management.” Clinical Diabetes. N.p., Oct. 2007. Web. 12 Apr. 2013.